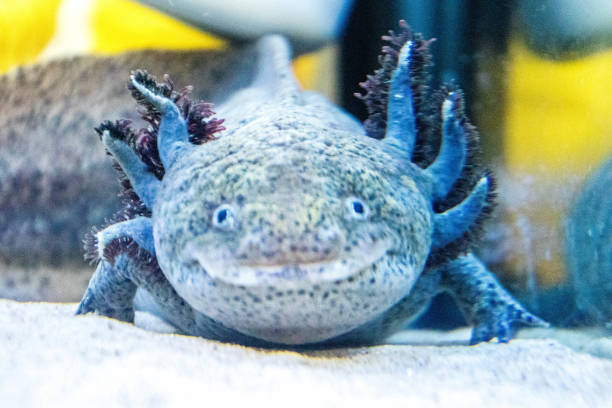
Hissing Cockroaches
Madagascar Hissing Cockroaches are known for the hissing sound they make by forcing air through spiracles, or respiratory openings, on their abdomen. This hiss can be made because of different situations: disturbance, mating, and fighting, but only males use the latter two. Another distinction between the two genders is the thicker antennae found on males. Unlike most cockroaches, these are wingless. Despite this, they are very good at climbing and can even climb up smooth glass.
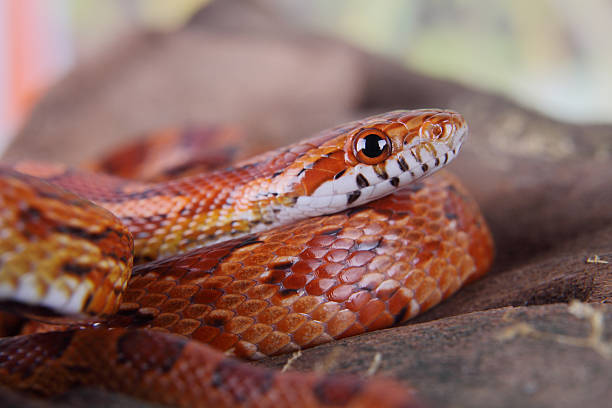



 Corn snakes (Pantherophis guttatus) are a species of rat snake native to North America. They are found predominantly in forests and woodlands of the southeastern US. These snakes make popular pets as they are docile, non-venomous, and come in a large variety of color and pattern morphs. Corn snakes reach 2-5 feet in length as adults and may live upwards of 20 years in captivity.
Corn snakes (Pantherophis guttatus) are a species of rat snake native to North America. They are found predominantly in forests and woodlands of the southeastern US. These snakes make popular pets as they are docile, non-venomous, and come in a large variety of color and pattern morphs. Corn snakes reach 2-5 feet in length as adults and may live upwards of 20 years in captivity.