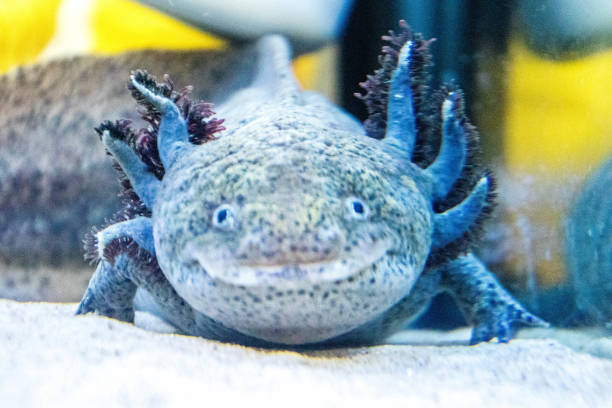
Basic Care: Axolotl
Background


Veterinary laser therapy is an innovative treatment that has gained popularity in recent years as veterinarians recognize how it benefits pets. Used similarly to acupuncture, massage therapy, and other alternative therapies, laser treatment can be used in conjunction with medication to manage pain, inflammation, and wound healing. Photobiomodulation (PBM) therapy results are achieved when a sufficient dose of light energy reaches target tissue and results in decreased inflammation, decreased pain, immune stimulation, and accelerated healing.
Ovarian cysts are fluid filled structures that develop on or near the ovary. There are many types of ovarian cysts and their prevalence in guinea pigs ranges from 58-100%. The two main types are 1) serous cysts, also known as nonfunctional or rete ovarii cysts, and 2) hormone producing follicular cysts. Rete cysts are non-hormone producing and typically do not cause clinical signs unless they are large and pushing on other organs. Follicular cysts develop from follicles on the ovary that fail to ovulate. When these types of cysts develop, the classic sign is non-itchy flank hair loss.
E. cuniculi-associated phacoclastic uveitis is a recognized disease in rabbits, particularly dwarf rabbits. There is no sex predilection and the condition is often seen in younger rabbits. The lesion occurs after rupture of the lens capsule releases lens protein into the anterior chamber, which results in granulomatous uveitis; however, the posterior chamber usually remains unaffected. The mass originates at the lens capsule, and the inflammation is centered on the break in the capsule.
Macrorhabdus ornithogaster, formerly known as “megabacteria,” is a Gram-positive yeast that affects psittacine (most commonly budgerigars) andsome non-psittacine birds.
Non-specific (“fluffed” bird), regurgitation, vomiting, loose stools, anorexia, chronic weight loss, emaciation, melena, anemia, sudden death. Birds are often acting hungry and eat readily despite weight loss.
Fecal cytology to identify the organism
Caution: can be easily washed of slides
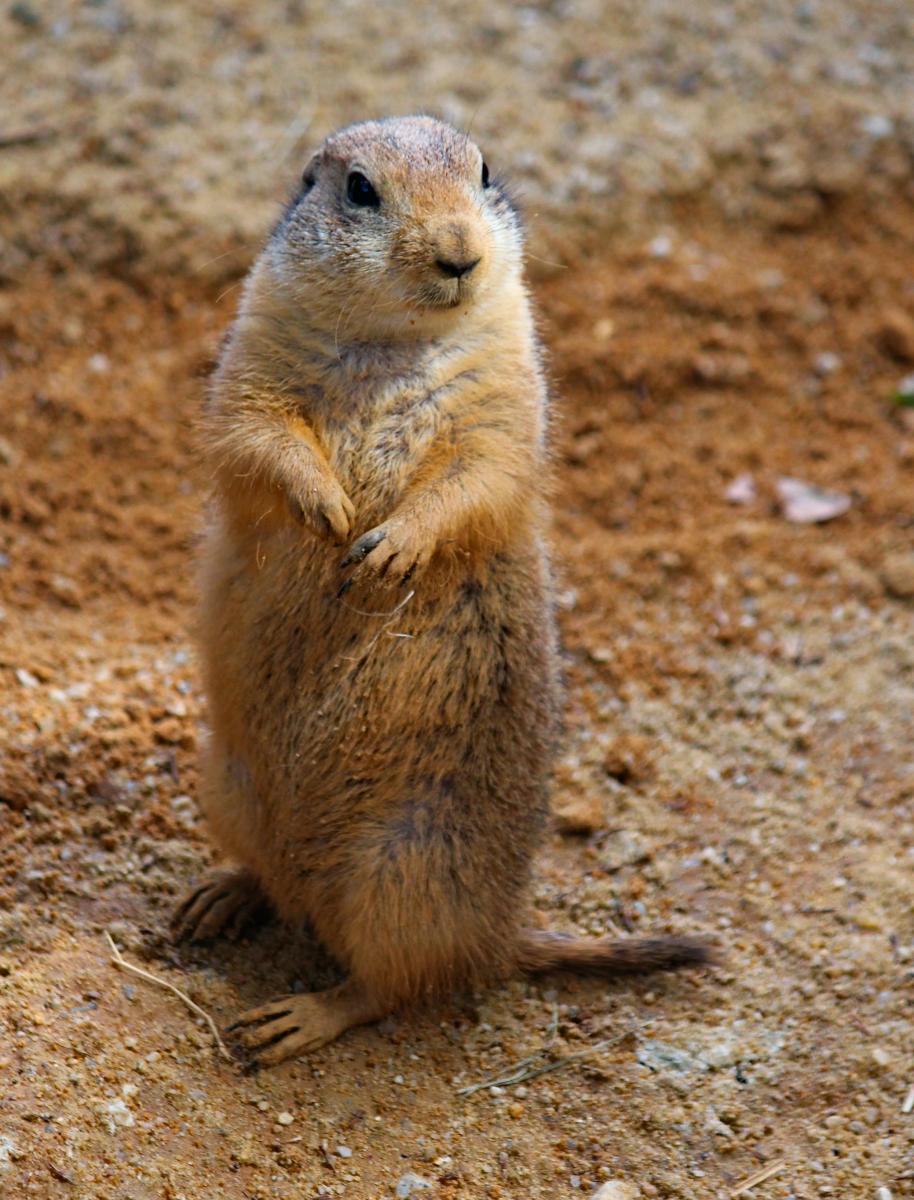

Found in the grass prairies of Mexico, Canada and through the central United States east of the Rocky Mountains.
Gout occurs because of a buildup of uric acid in the blood. This can result in being deposited in the joints, which is called articular gout, or in the organs, which is called visceral gout. This can occur either because of the body producing too much uric acid or from the body not being able to get rid of the uric acid.
Rabbits that are unintentionally urinating on themselves or sitting in their own urine for prolonged periods can develop urine scald. Urine scald occurs when urine is left to soak onto the fur and skin which results in fur loss, inflammation and/or ulceration and infection (burning) of the skin.
As rabbits age, it is common for them to develop conditions that make it challenging for them to go about day-to-day activities. Most commonly, rabbits will develop osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease making it difficult for them to ambulate and groom themselves. Osteoarthritis is a painful condition of the joints that results in inflammation and a decreased range of motion. Most affected joint spaces are the knees (stifles) and the area where the spine meets the pelvis (lumbosacral).
Pellets should make up the foundation of a healthy parrots diet (60-80% of the total diet), but there are a number of healthy foods you can also offer to provide not only balanced nutrition but give your bird something fun to eat and enjoy. Here is a list of healthy food options for your bird.