Calcium Deficiency in Sugar Gliders
Calcium deficiency leading to nutritional secondary hyperparathyroidism (NSHP) is one of the most common problems of sugar gliders. NSHP, sometimes known as metabolic bone disease or MBD, is very common in young growing gliders fed an improper diet. The diet may be deficient in calcium, have too much phosphorus, not enough vitamin D3, or some combination of these problems. The bones never mineralize, and end up weak and easily broken. A sugar glider on a bad diet may appear perfectly normal right up until the time you find it paralyzed at the bottom of it's cage due to a broken back. S


 Rabbits sometimes develop a head tilt that gets progressively worse until they roll uncontrollably when they try to move. This condition is commonly known as "wry neck". There are many different diseases that can cause wry neck such as an ear infection, a parasite known as Encephalitozoon cunniculi (often just called E. cunniculi or encephalitozoonosis), and others. Depending on the cause, treatment is often quite successful if initiated early. Sometimes the treatment arrests the underlying disease but the rabbit continues to have a head tilt. Most of these learn how to live with their new view of the world and many gradually return to almost a normal posture.
Rabbits sometimes develop a head tilt that gets progressively worse until they roll uncontrollably when they try to move. This condition is commonly known as "wry neck". There are many different diseases that can cause wry neck such as an ear infection, a parasite known as Encephalitozoon cunniculi (often just called E. cunniculi or encephalitozoonosis), and others. Depending on the cause, treatment is often quite successful if initiated early. Sometimes the treatment arrests the underlying disease but the rabbit continues to have a head tilt. Most of these learn how to live with their new view of the world and many gradually return to almost a normal posture.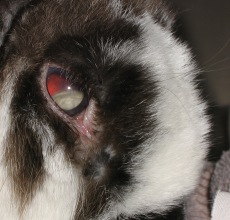 Rabbits often develop a cloudy appearance to their eyes. The eyes may become cloudy on the cornea (surface of the eye), the lenses, or any of the chambers inside. There may be many different causes for this disorder ranging from a parasite, Encephalitozoon cunniculi, to a corneal scratch or ulcer, cataracts, or various infections. A rabbit eye can quickly get damaged beyond repair so any time you see a change in an eye, a health consulta
Rabbits often develop a cloudy appearance to their eyes. The eyes may become cloudy on the cornea (surface of the eye), the lenses, or any of the chambers inside. There may be many different causes for this disorder ranging from a parasite, Encephalitozoon cunniculi, to a corneal scratch or ulcer, cataracts, or various infections. A rabbit eye can quickly get damaged beyond repair so any time you see a change in an eye, a health consulta